Identifying Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the general name for a group of cardiovascular diseases, mainly atherosclerotic heart disease. It is a progressive condition that impairs your ability to maintain normal blood circulation, increasing your risk of heart attack and stroke. At a young age, atherosclerosis occurs only in people who have hereditary atherosclerosis in the family. With age, atherosclerosis can occur in other parts of the body, but most often in the heart. Therefore, it is very important that people aged 40 and over seek help from their doctor as soon as possible.
Atherosclerosis is a disease of the arteries. The walls of your arteries are made up of multiple layers. They are composed of plaque fat, which forms as a result of the plaque-forming activity of the arteries, and fibrous plaques, which can form due to the plaque-forming activity or other factors.
A disease known as atherosclerosis is commonly referred to as “atherosclerosis of the heart,” an atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. This is because atherosclerosis is a symptom of a more serious underlying disease. The heart is not the only part of your body that may be suffering from atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a relatively new disease. Early treatment of atherosclerosis was difficult. However, with the advancement of science, it has become easier to treat atherosclerosis and even reverse its effects. Most current treatment options include medications, surgery, and medical procedures. Treatment options range from reducing plaque build-up to addressing the underlying cause of the disease.
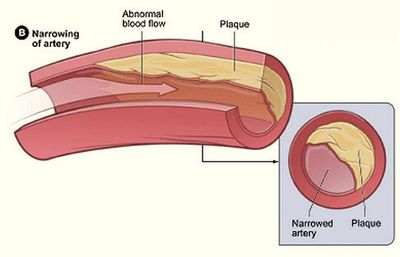
Atherosclerosis occurs when plaque builds up on the inner walls of the arteries, preventing the arteries from carrying blood away from the heart. When this happens, cholesterol or fat from your body begins to build up in the walls of your arteries. When your blood flows through your arteries, some of the fat builds up. The accumulation of fat causes the walls of the arteries to harden, and this hardening leads to calcification of the arteries. Eventually, the walls of the arteries can no longer provide adequate blood flow to your heart, and your heart condition worsens.
Atherosclerosis can also be caused by a buildup of plaque in the arteries, known as arterial atherosclerosis. arterial cancer atherosclerosis is much less serious than atherosclerosis. When your arteries become calcified, the buildup of calcium deposits leads to the formation of plaque that can block the arteries. Then the walls of the arteries thicken and the heart’s ability to pump blood through the arteries is weakened. Arteriosclerosis usually has no symptoms. However, due to the complexity of atherosclerosis symptoms, treatment options include surgery, medication, and lifestyle changes.
If you have a family history of heart disease, it is important to get treatment. Although it is a progressive disease, it can be controlled. However, if you are younger than 40 and do not have an increased risk of heart disease, treatment may not be necessary if you have not had heart or blood vessel problems in the past. Treatment for atherosclerosis will depend on the specific type of atherosclerosis you have. Treating atherosclerosis now can prevent the disease from progressing to heart failure and also increase your chances of prevention. More information about heart disease can be found on the website Bupa.co.th
Symptoms of atherosclerosis vary from person to person. If you smoke, you should consider quitting smoking. Smoking reduces the effectiveness of treatment for arteriosclerosis. Other treatments, such as reducing plaque and preventing atherosclerosis, can help you avoid these symptoms. In most cases, after you are diagnosed with atherosclerosis, treatment can be started as soon as the diagnosis is made, but this depends on the severity of your condition.