Types of Denial of Service Attacks
In computer networks and even in computers themselves, an attack is usually any attempt to corrupt, degrade, manipulate, disrupt, break, steal, obtain access to or otherwise make unauthorized use of some asset. The term attack has a variety of meanings which can be applied to different ways of compromising a system. In general, an attack is typically defined as any action that results in the compromise of some aspect of the network system. Attacks can be classified into logical or physical attacks.
Logical attacks can occur if something in the network is corrupted or compromised such as software or hardware. Physical attacks are the most common type of attack and are more difficult to defend against because they require the attacker to physically penetrate into the system. There are a number of ways by which physical attacks can be carried out. Some common physical attacks include:
One of the most popular types of physical attacks is through security holes. Security holes are holes in the system's configuration that allow an intruder to access an application, device, database, etc. In most cases, an intruder will first identify a target of interest and attempt to access it through a security hole.
Some common forms of security holes are:
- A Trojan is a program designed to infect a user's machine by compromising a particular type of system's configuration files. These types of attacks are generally considered a form of spear-phishing.
- Key loggers are programs that monitor keystrokes and passwords for purposes of sending this information to remote servers for further use or sending it to other attackers. Some commonly used key loggers include keylogger remover.
- Malware is software that can be installed on a computer without the permission of the user.
Malware generally does things like:
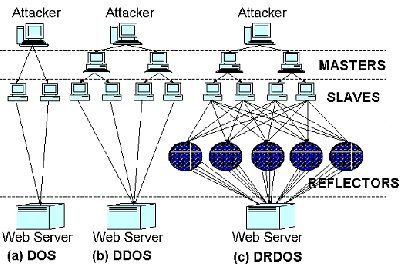
Attackers can also perform a number of various methods of denial of service attacks. A common denial of service attack is known as a SYN flood where an attacker floods a network with SYN packets to overload or clog up a server.
This can result in the server being unable to communicate with other machines or services
Other common types of denial of service include:
- Denial of Service attacks can also occur when a network is overloaded with data. When a large amount of data is present, it takes longer to transmit these messages back and forth. The result is that users experience increased delay in processing data and may experience a loss of performance and reliability in the network. This can be particularly serious if the attacker uses their own internal resources to carry out an attack.
- Spam is unwanted e-mails sent through an e-mail system. Spamming involves flooding an e-mail server with junk mail in order to get people to open the message and forward it to others who have more important matters to deal with. If the recipient of the spam e-mail is not interested in the message, it can cause a significant impact to the recipient's reputation and can even bring down the e-mail system itself.
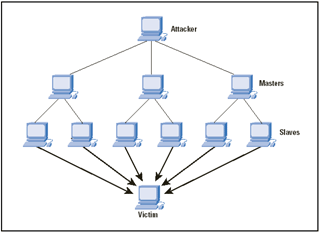
- Denial of Service attacks can also occur in other forms of networks. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks is where a large number of IP addresses are attacked at one time to bring down a server. Another example of a DDoS attack is called Distributed Denial of Service attack (DDoS) where hundreds of network users connect to the same server, causing it to go offline.
A network administrator's responsibility is to stop attacks before they reach an impact on the system. Some common denial of service attacks include:
Attacks can also occur while a system is unplugged, asleep, or off, such as if a computer is turned off while at home. However, attackers need to have access to a computer in order to be able to perform a denial of service attack because unplugging a computer will not prevent it.
A network administrator's responsibility is to detect and stop attacks before they have a chance to affect the network. It is advisable for network administrators to have a dedicated network monitoring service to be able to monitor the status of the network and stop attacks from occurring before they can do any damage.
While a network administrator's responsibility is to prevent attacks, the company's responsibility is to react quickly to prevent the attacks from happening in the first place. This is usually done through monitoring and maintenance. If an attacker tries to gain access to a company's network, an alert will be sent to an administrator to advise them of the attempt so they can take steps to stop it.